Compose Multiplatform bridging the Platform Divide: using Expect/Actual mechanism
Compose Multiplatform bridging the Platform Divide: using Expect/Actual mechanism
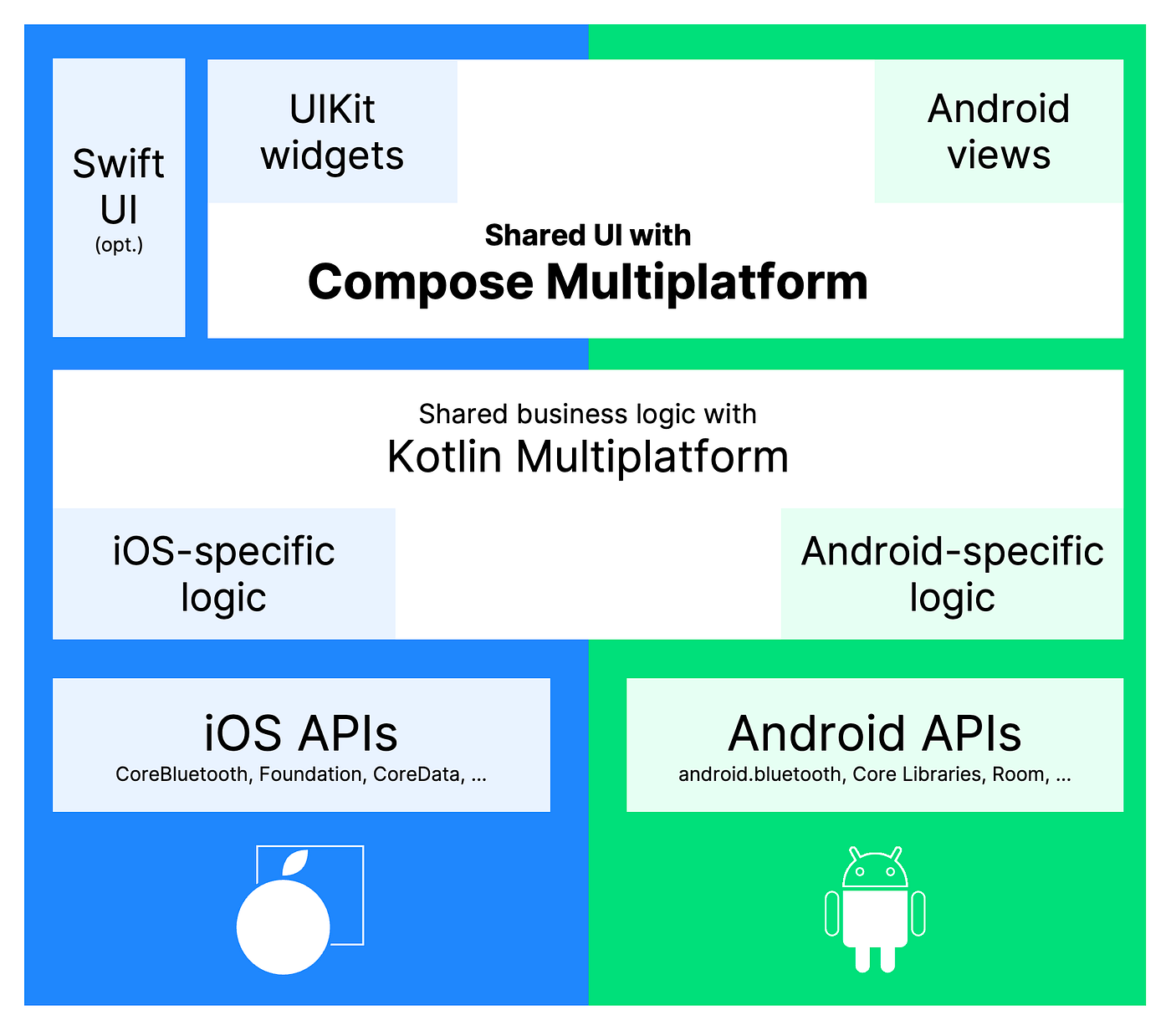
Compose Multiplatform lets you create stunning UIs for Android, iOS, Desktop, and Web. With the expect/actual mechanism, you can write shared logic while tailoring platform-specific logics seamlessly.
🚀 Understanding Expect/Actual in Kotlin Multiplatform
The expect/actual mechanism makes cross-platform magic happen! 🪄
expect: Declare a function or property in common code that needs platform-specific handling.actual: Define how it works on each platform (Android, iOS, etc.).
Write shared logic, let platforms handle the rest.
🎯 Benefits of Expect/Actual
1️⃣ Shared Codebase: Write core logic once and reuse it across platforms, saving time and effort.
2️⃣ Native Specific: Use platform-specific components for the best user experience.
3️⃣ Better Testing: Keep platform logic separate, making it easier to test your shared code.
Example 1. Sample Code for a Cross-Platform Local DateTime Formatting
Common Code (commonMain/com/example/DateTime.kt):**
expect object DateTime {
fun LocalDateTime.format(format: String): String
fun getDateTime(string: String, format: String): LocalDateTime
}
Android Code (androidMain/com/example/DateTime.kt):
actual object DateTime {
actual fun LocalDateTime.format(
format: String
): String =
SimpleDateFormat(format, Locale.getDefault()).format(
toJavaLocalDateTime().toKotlinLocalDateTime().toInstant(
TimeZone.currentSystemDefault()
).toEpochMilliseconds()
)
@SuppressLint("NewApi")
actual fun getDateTime(string: String, format: String): LocalDateTime {
val formatter = DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern(format)
val zonedDateTime = ZonedDateTime.parse(string, formatter)
return zonedDateTime.toLocalDateTime().toKotlinLocalDateTime()
}
}
iOS Code (iosMain/com/example/DateTime.kt):
actual object DateTime {
actual fun LocalDateTime.format(format: String): String {
val dateFormatter = NSDateFormatter()
dateFormatter.dateFormat = format
return dateFormatter.stringFromDate(this.toInstant(TimeZone.currentSystemDefault()).toNSDate())
}
actual fun getDateTime(string: String, format: String): LocalDateTime {
val dateFormatter = NSDateFormatter()
dateFormatter.dateFormat = format
val date = dateFormatter.dateFromString(string)
?: throw IllegalStateException("Could not convert string to NSDate $string")
return date.toKotlinInstant().toLocalDateTime(TimeZone.currentSystemDefault())
}
}
Usage:
val today = getLocalDateTimeFromLong(getCurrentLocalTimestamp()).format("dd.MM.yyyy hh:mm a")
In your composable screens within the common codebase, you can use the DateTime formatting and getDateTime functions with your desired formats.
Example 2. Sample Code for a Cross-Platform decimal formatting
Common Code (commonMain/com/example/Formatter.kt):
expect fun formatNumber(number: Double): String
Android Code (androidMain/com/example/Formatter.kt):
import java.text.DecimalFormat
actual fun formatNumber (number: Double): String{
val formatter = DecimalFormat("#,###")
return formatter.format(number)
}
iOS Code (iosMain/com/example/Formatter.kt):
import platform.Foundation.NSNumber
import platform.Foundation.NSNumberFormatter
import platform.Foundation.NSNumberFormatterDecimalStyle
actual fun formatNumber (number: Double): String{
val numberFormatter = NSNumberFormatter()
numberFormatter.numberStyle = NSNumberFormatterDecimalStyle
return numberFormatter.stringFromNumber(NSNumber(number)) ?: ""
}
Usage:
Text(
text = formatNumber(item().value), // Decimal
style = MaterialTheme.typography.bodyMedium,
color = MaterialTheme.colorScheme.onPrimary,
fontWeight = FontWeight.Bold,
maxLines = 1,
overflow = TextOverflow.Ellipsis
)
In your composable screens within the common codebase, you can call the formatNumber function with your desired values. The platform-specific implementation will seamlessly handle.
Conclusion:
The expect/actual mechanism helps you build efficient and easy-to-maintain cross-platform apps with Compose Multiplatform. By following these tips and learning the core ideas, you can smoothly connect platforms and create a great experience for users on any device.
💡 #Kotlin #Compose #Multiplatform #DevTips
